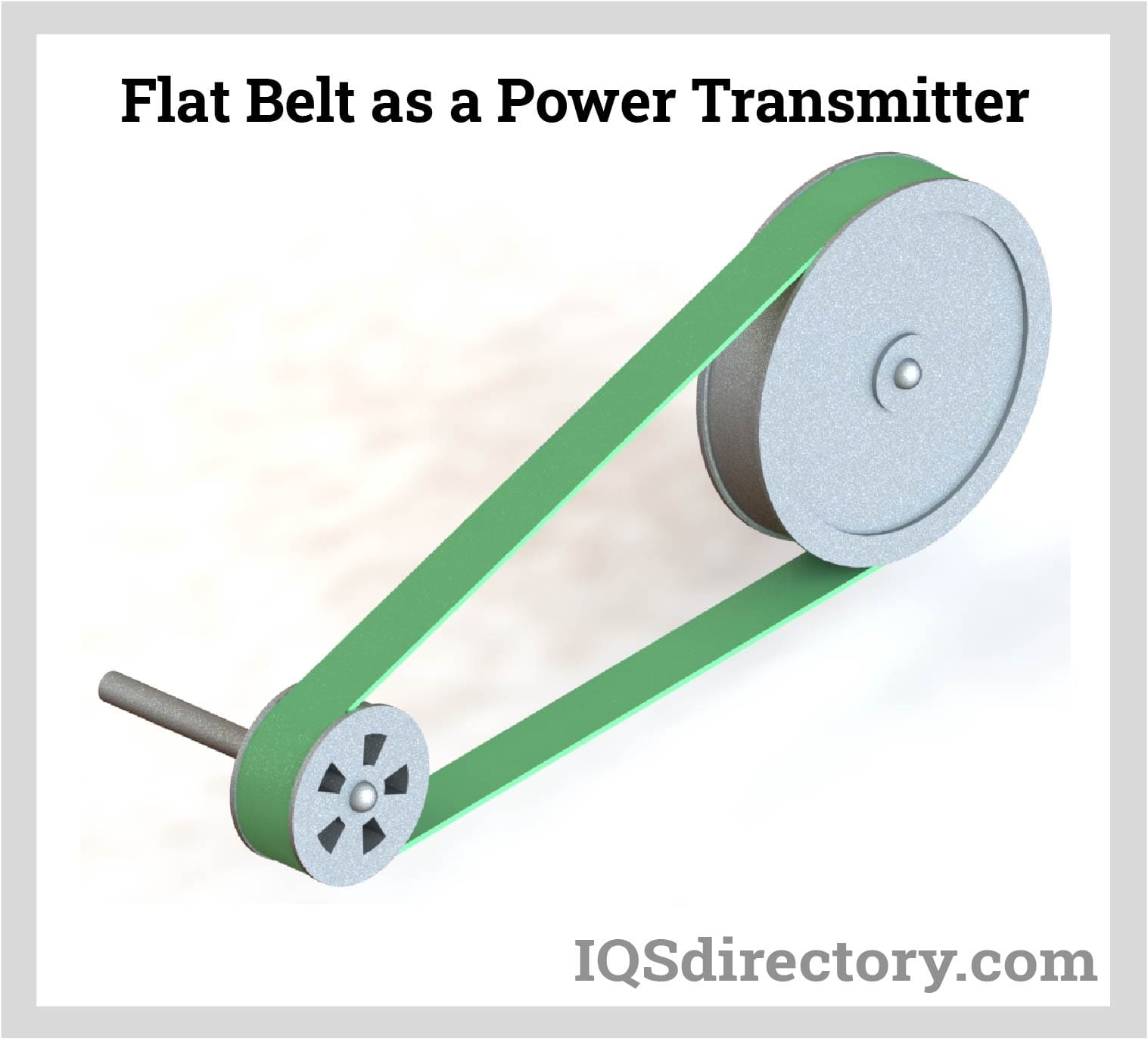
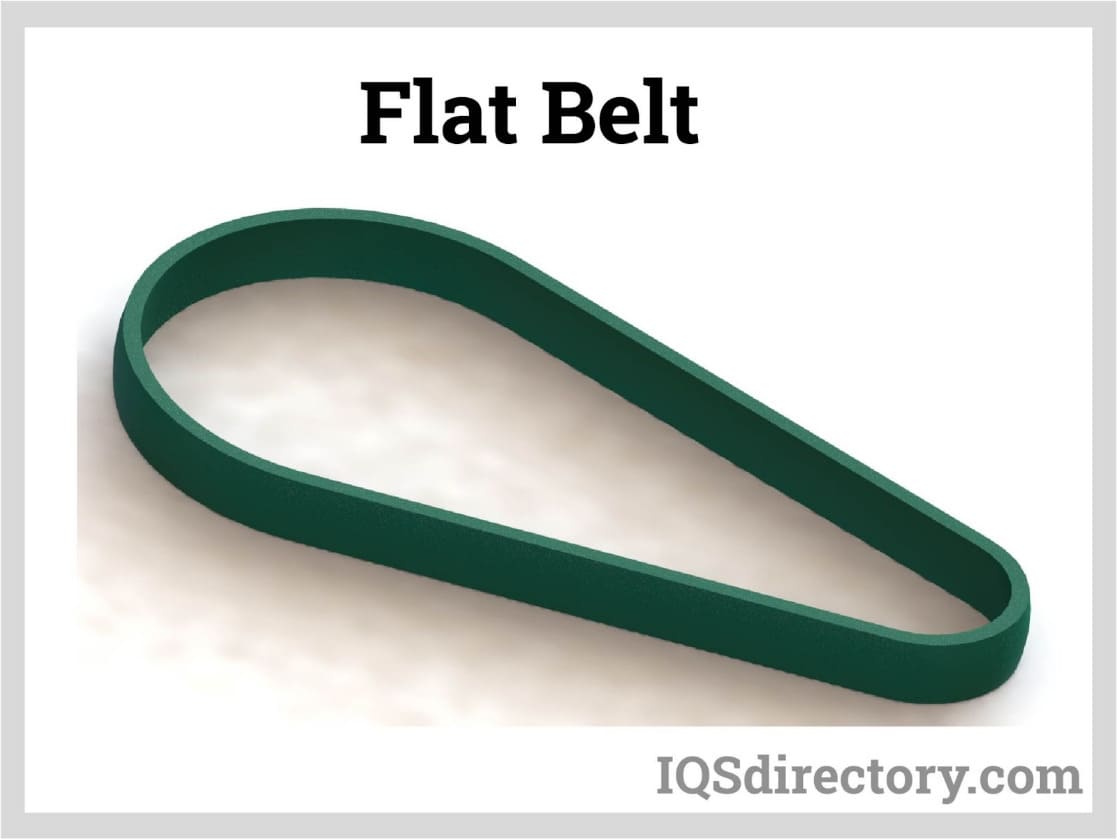
Flat belts may be used as part of conveyance systems to move things directly by directly setting items upon them. A continuous flat belt may be made of either natural or synthetic cloth (ex., polyester, nylon) and is paired with several motorized pulleys to form a conveyor. Read More…
We have a wide range of products that allow us to find the right solutions for all our customer’s material handling needs. We provide conveyor belts made out of variety of materials. Our research and development department works hard to ensure that we are bringing our customers products that are on the leading edge of innovations at all times. For more information on how we may be able to...
For more than 60 years, we have been offering innovative conveyor belting to customers worldwide. Our full line of products include perforated belts, vacuum belts, nylon core belts, and plastic modular belting. We have grown our reputation based on providing outstanding customer service as well as conveyor belt materials that will provide long-lasting value. For more information on how we may be...

At Shipp Belting, we specialize in manufacturing and distributing high-quality conveyor belts designed to meet the diverse needs of industrial operations. With decades of experience behind us, we’ve built our reputation on reliability, technical expertise, and a deep understanding of how material handling impacts overall efficiency.

Fenner Dunlop Americas has built a reputation in belt manufacturing, and our goal is to find the perfect solution for you. Our staff is dedicated to your needs and we are capable of assisting you in finding the belt your application requires. To learn more about the details of our industrial belts then simply visit our website or give one of our representatives a call.
More Flat Belt Manufacturers
Flat belts are a fundamental component of many industrial and manufacturing systems, renowned for their reliability and efficiency in power transmission and material handling. These belts are often integrated with motorized pulleys to drive various types of machinery, making them a popular choice across an array of applications. Additionally, optional features such as center drives and nose bars can be incorporated into flat belt systems to suit specific operational requirements, enhancing versatility and performance.

Material of Flat Belts: Exploring Construction and Material Choices
One of the primary reasons for the widespread adoption of flat belts in conveyor systems and industrial applications is their adaptability in terms of material selection. The choice of material is crucial, as it directly impacts the belt’s durability, flexibility, resistance to environmental factors, and overall suitability for a given application. When evaluating flat belts, buyers often consider the substance, width, thickness, and performance properties required for their particular use case.
Common Flat Belt Materials and Their Use Cases
- Natural Rubber: While natural rubber offers excellent flexibility, it is generally unsuitable for high-temperature or high-load environments. Narrow flat belts made from natural rubber are rarely used in heat-treating or heavy-duty conveyor applications due to their limited heat resistance and load-bearing capabilities.
- Synthetic Rubber: For operations requiring enhanced heat resistance and longevity, synthetic rubber is often preferred. Heat-resistant synthetic rubber flat belts are ideal for manufacturing lines, packaging, and processing plants where exposure to elevated temperatures is common.
- Plastic Belts: Plastics such as PVC and polyurethane (PU) are frequently used in conveyor belt fabrication due to their chemical resistance, ease of cleaning, and suitability for food processing, pharmaceutical, and light manufacturing applications.
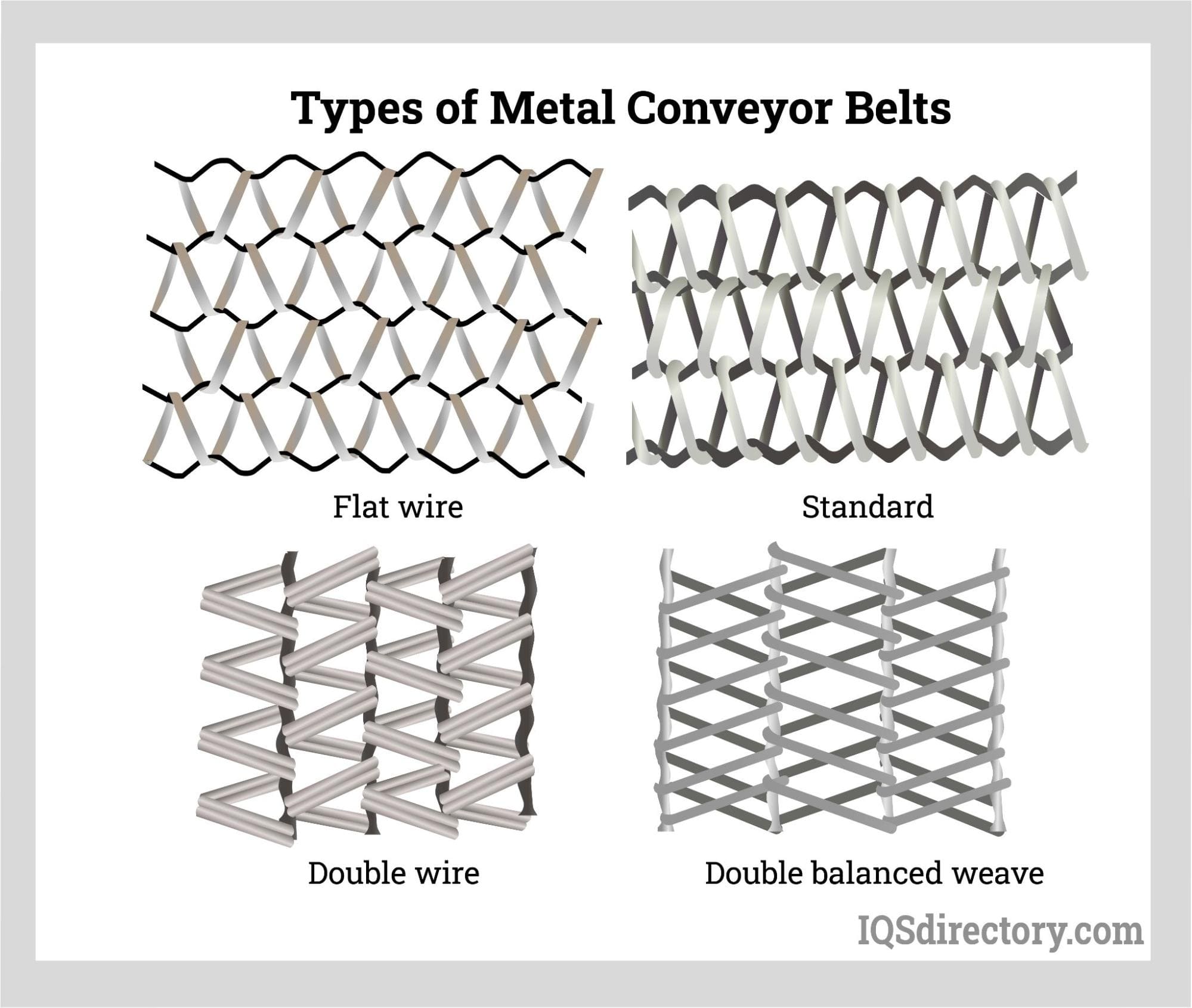
- Metal Flat Belts: For applications involving extreme temperatures, abrasive materials, or heavy loads, metal belts (such as stainless steel) are preferred. These belts are commonly found in baking ovens, heat treating lines, and other demanding environments where conventional materials might fail.
- Other Materials: Neoprene, silicone, nylon, and Teflon™ (PTFE) are also used for specialized requirements. For example, silicone and Teflon™ offer high temperature and non-stick properties, making them suitable for the electronics, packaging, and textile industries.
Selecting the right flat belt material is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Each material is engineered for specific operational parameters, such as load capacity, abrasion resistance, chemical compatibility, and temperature tolerance. If you’re unsure about which material best fits your conveyor system or machinery, consult with an experienced conveyor belt supplier or flat belt manufacturer for tailored guidance.

Common Problems Encountered With Flat Belts and Troubleshooting Solutions
Like all industrial components, flat belts can encounter operational issues that impact productivity, cause downtime, or lead to premature wear. Understanding these common problems and their respective solutions is vital for maintenance professionals and engineers aiming to maximize conveyor uptime and minimize repair costs.
- The conveyor runs to one side at a specific location on the structure.
Potential Causes:
- Material buildup on idlers (pulleys used to guide the belt)
- Stuck idlers
- Idlers or pulleys misaligned with the belt’s centerline
- Misaligned conveyor frame or supporting structure
- Idler feet not centered on the belt
- Unleveled structure
Recommended Solutions:
- Remove buildup and implement regular cleaning protocols with scrapers or automated cleaning equipment.
- Free stuck idlers and enhance lubrication and maintenance routines.
- Realign idlers and pulleys to ensure they are parallel and centered relative to the belt’s path.
- Straighten or reinforce structural sections as needed.
- Adjust idler feet and level the conveyor structure for improved tracking.
- On the conveyor, a specific belt segment always runs to one side.
Potential Causes:
- Belt not squarely spliced or connected
- Belt is bowed due to improper storage or handling
Recommended Solutions:
- Re-splice the belt and remove the damaged splice to restore proper alignment.
- Allow new belts to break in; if the issue persists, straighten or replace the belt and review storage protocols.
- The conveyor’s full length or a significant portion of the belt runs to the side.
Potential Causes:
- Belt swerving across the loading region and around the tail pulley
- Poorly centered or off-center loading
- Material buildup on idlers
- Idlers or pulleys not aligned with the belt’s centerline
- Misaligned conveyor frame
Recommended Solutions:
- Install training idlers on the return side before the tail pulley to stabilize belt tracking.
- Adjust loading chutes to center the load and discharge material at or near belt speed.
- Maintain clean idlers and use scrapers or cleaning devices to prevent buildup.
- Realign idlers, pulleys, and supporting structures where necessary.
Proactive maintenance of conveyor belt systems—including tracking adjustments, regular cleaning, and proper storage—can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of these issues. Are you troubleshooting persistent flat belt problems? Contact a conveyor system specialist or explore our maintenance resource center for detailed guides and expert advice.
Applications of Flat Belts: Industry Uses and Innovative Solutions
Flat belts are among the most versatile conveyor belt types, supporting diverse industries and applications. Their simple design, efficient power transmission, and compatibility with a wide range of accessories make them suitable for everything from light-duty conveying to heavy industrial transport.
Industrial Sectors Utilizing Flat Belts
- Manufacturing: Flat belts are extensively used in assembly lines, packaging facilities, and automated production systems for the efficient movement of goods, parts, and finished products.
- Agriculture: From threshing machines and grain conveyors to balers, silo blowers, and irrigation pumps, agricultural operations rely on flat belts for dependable mechanical power transmission and material handling.
- Mining and Logging: Mining conveyors and logging equipment use heavy-duty flat belts to move ores, aggregates, timber, and other bulk materials under demanding conditions.
- Food Processing: Flat belts with food-grade materials and hygienic coatings are used in bakeries, canneries, meat processing plants, and bottling lines to ensure sanitary, efficient transport.
- Automotive and Electronics: Flat belts play a crucial role in conveying components along assembly lines, robotic workstations, and parts inspection stations in automotive and electronics manufacturing.
- Textile and Printing: Flat belts facilitate precise movement of fabrics, paper, and materials in textile looms, printing presses, and finishing equipment.
- Material Handling and Warehousing: Distribution centers and warehouses use flat belt conveyors to transport packages, boxes, and pallets between sorting and shipping areas, optimizing logistics efficiency.
Special Features and Customizations for Flat Belts
To address unique operational demands, flat belts can be customized with a variety of enhancements, such as:
- Cleats or profiles for positive drive and improved grip
- Laminations and surface coatings for increased durability or reduced friction
- Perforations for air flow or vacuum applications
- Sidewalls to contain loose materials during transport
- Antistatic or flame-retardant properties for sensitive environments
Flat belts are available in both endless (seamless) and joined (seamed) configurations, allowing users to select the best fit for their conveyor system layout, maintenance preferences, and operational requirements. Whether you need a simple replacement belt or a fully customized solution, partnering with a reputable flat belt manufacturer is essential for reliability and long-term performance.
Benefits of Flat Belts: Why Choose Flat Belt Conveyors?
When comparing conveyor belt types, flat belts offer several distinct advantages that make them an attractive choice for many operations. Key benefits include:
- Energy Efficiency: Flat belts minimize friction losses, resulting in lower power consumption and operational costs compared to other transmission systems.
- Quiet Operation: Their smooth surface and seamless integration with pulleys ensure quiet, vibration-free performance, ideal for noise-sensitive environments.
- Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and simple tracking adjustment, flat belts require less maintenance than chain or modular belts.
- Versatility: Suitable for both light and heavy loads, flat belts accommodate a broad range of applications, from delicate electronics to heavy industrial goods.
- Customizability: A wide selection of materials, surface finishes, and accessories allows for tailor-made solutions to meet specific operational needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Flat belts generally offer a lower initial investment and long service life, contributing to overall cost savings.
Decision Factors: How to Select the Right Flat Belt for Your Application
Choosing the optimal flat belt involves careful assessment of application requirements, environmental factors, and long-term maintenance considerations. Here are key decision factors to guide your selection process:
- Load Requirements: Evaluate belt strength, thickness, and material composition to ensure adequate support for your products or materials.
- Operating Environment: Consider temperature extremes, moisture levels, exposure to chemicals, and hygiene requirements when selecting belt materials and coatings.
- Speed and Power Transmission: Match the belt’s speed rating and tension capacity to your conveyor drive system for optimal efficiency and safety.
- Tracking and Alignment: Look for belts with reinforced edges or specialized tracking guides to maintain consistent, centered movement throughout operation.
- Maintenance and Serviceability: Choose belts that are easy to install, inspect, clean, and replace, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions.
- Supplier Support: Partner with a reputable manufacturer or distributor that offers technical support, custom engineering, and rapid turnaround on orders.
Choosing the Proper Flat Belts Manufacturer: Find the Right Supplier for Your Needs
Partnering with the right flat belt manufacturer or supplier is crucial to ensuring product quality, dependable supply chains, and responsive customer service. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help you find the best provider for your flat belt, conveyor belt, or power transmission belt needs:
- Research and Compare Suppliers: Start by identifying at least six reputable flat belt manufacturers using our manufacturer directory. Review each company’s business profile, capabilities, and industry experience to gauge their suitability for your project.
- Evaluate Product Offerings: Assess the range of flat belt types, materials, customization options, and value-added services each supplier provides. Consider whether they offer food-grade, heat-resistant, antistatic, or specialty conveyor belts tailored to your sector.
- Request Quotes and Technical Information: Use the contact forms provided on supplier profile pages to request detailed quotes, product specifications, or engineering support. Leverage our simple RFQ (Request for Quote) tool to reach multiple manufacturers simultaneously and compare pricing, lead times, and technical advice.
- Review Customer Support and Service: Investigate after-sales support, warranty terms, and available resources for installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. A responsive supplier will help you minimize downtime and maximize ROI.
- Leverage Online Resources: Utilize our patented website previewer to explore supplier websites, review case studies, and evaluate customer testimonials for added confidence in your purchasing decision.
Ready to source high-quality flat belts? Request a quote today or reach out to our team for personalized assistance with your flat belt selection, installation, and maintenance needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Flat Belts
- What is a flat belt? A flat belt is a flexible, continuous loop used for mechanical power transmission or material handling, widely used in conveyor systems, industrial machinery, and agricultural equipment.
- How do I choose the right flat belt material? Consider factors such as load, speed, temperature, chemical exposure, and hygiene. Refer to our material guide or consult an expert for tailored recommendations.
- How can I prevent tracking issues with flat belts? Ensure proper installation, maintain alignment of pulleys and idlers, and implement regular cleaning and inspection protocols.
- Are flat belts suitable for food processing? Yes, food-grade flat belts made from approved materials like PVC or polyurethane are ideal for sanitary food handling applications.
- Where can I buy flat belts online? Use our supplier directory to find trusted flat belt manufacturers and distributors.
Get Expert Help with Flat Belts and Conveyor Systems
Whether you’re upgrading an existing conveyor system, specifying a flat belt for a new application, or troubleshooting operational issues, our team of industry experts is here to help. Explore our in-depth industry guides, product selectors, and technical resources to make informed decisions that drive productivity and value.
Have a specific question or need a custom solution? Contact us for personalized assistance—our engineers and support staff are dedicated to your success.










 Conveyor Belting
Conveyor Belting Conveyor Systems
Conveyor Systems Conveyors
Conveyors Hosereels
Hosereels Industrial Lubricants
Industrial Lubricants Lubricators
Lubricators Screw Conveyors
Screw Conveyors Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic Conveyors AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches