More Conveyor Belt Manufacturers
Conveyor Belting Applications: Enhancing Efficiency Across Industries
Conveyor belting systems are the backbone of efficient material handling in countless commercial and industrial environments. At Conveyorbelting.net, we provide high-quality conveyor belts designed to streamline operations, reduce production times, and minimize labor costs. From factory assembly lines to small retail checkout counters, our conveyor solutions ensure seamless movement of goods, making them indispensable across virtually every industry. Discover how our conveyor belting systems can transform your operations.
What Are Conveyor Belt Systems?
Conveyor belt systems are mechanical assemblies engineered to transport goods, products, and materials from one point to another with ease. These systems excel in moving heavy items, mass-produced products, and even hazardous materials, making them a critical asset in industries like:
- Automotive: For assembly line efficiency.
- Mining: To transport ores and bulk materials.
- Electronics: For precise handling of components.
- Food Processing: Ensuring hygiene and safety.
- Textiles, Packaging, Pharmaceuticals, and More: For streamlined material flow.
Conveyor belts are designed to meet the unique demands of these industries, ensuring reliable performance and durability.
How Conveyor Belts Work
A conveyor belt operates as a continuous loop stretched between two end-pulleys, powered by a motor to move materials at varying speeds. These belts are typically made from durable materials such as:
- Rubber: For flexibility and grip.
- Fabric: For lightweight applications.
- Leather, Plastic, and Metal: For specialized needs.
- Steel: For heavy-duty tasks, ideal for bulk material handling.
For larger or heavier loads, a thicker, stronger belt is essential. Troughed belt conveyors, available at Conveyorbelting.net, are perfect for handling bulk or heavy items like gravel, coal, or grain, ensuring efficient transport without spillage.
Types of Conveyor Belts and Their Applications
Here is a range of conveyor belt types to suit diverse applications:
- Belt Conveyors: The simplest and most versatile type, using a motor and pulley system to create a continuous loop. They’re ideal for:
- General Material Handling: Moving packages within a factory.
- Bulk Material Handling: Transporting large quantities of resources like salt, gravel, or coal.
- Plastic Modular Belts: Perfect for food processing, offering flexibility and easy maintenance.
- Solid Flat Belts: Used in both primary and secondary food processing for smooth, hygienic transport.
- Wire Mesh Belts: Ideal for high-temperature or heavy-duty applications, such as in food and beverage processing.
- Belt Conveyors: The simplest and most versatile type, using a motor and pulley system to create a continuous loop. They’re ideal for:
Our steel conveyor belts are engineered for durability, making them the go-to choice for handling substantial loads and challenging bulk materials in industries like mining and waste management.
Industries That Rely on Conveyor Belting
Conveyor belts are essential across a wide range of sectors, including:
- Food and Beverage Processing: Ensuring product safety and quality with hygienic belts like Plastic Modular and Wire Mesh.
- Pharmaceuticals: For precise and contamination-free handling.
- Waste Management: To sort and transport materials efficiently.
- Milling, Mail Sorting, and Printing: For streamlined operations.
- Engines and Machinery: Conveyor systems are integral to various mechanical setups.
Without conveyor belting, these industries would face inefficiencies, relying on manual labor to move and sort goods, which significantly increases operational time and costs.
Maximizing Efficiency with Conveyor Belting
To maximize productivity, it’s crucial to maintain your conveyor belt system and prevent downtime. A well-maintained conveyor belt splice is key to ensuring uninterrupted operation, avoiding costly repairs and financial losses. IQSdirectory provides guidance on maintaining your conveyor systems, ensuring long-term efficiency and reliability.
History of Conveyor Belting
Conveyor belt systems started to appear in manufacturing towards the end of the 1700s. The earliest known example was introduced in 1795, featuring a wooden slider bed, a leather belt, pulleys, and a hand crank. This early conveyor was utilized by seamen and merchants for loading products and goods onto ships. By 1804, the British Navy had commissioned the development of a steam-powered conveyor, designed to help their cooks efficiently bake biscuits.
After a period of dormancy, conveyor systems saw a revival in the late 1800s, driven by the needs of miners and the growing automotive industry. In 1892, American inventor Thomas Robins, commissioned by Thomas Edison, developed a conveyor belt designed to efficiently transport coal and ore from Edison’s mining operations. Robins’ design featured a leather belt with wire-sewn segments. This innovation proved highly successful, earning first prizes at both the Saint Louis Exposition and the Pan-American Exposition, and the grand prize at the 1900 Paris Exposition.
In 1901, a Swedish company named Sandvik introduced a steel conveyor designed for transporting gravel. Then, in 1905, Richard Sutcliffe, an Irish miner who had transitioned to engineering, invented the first underground conveyor. This innovation revolutionized mining by dramatically reducing the labor needed to move materials from the mine to the surface. Only three years later, engineers unveiled the roller conveyor, further advancing the field.
In 1913, Henry Ford revolutionized manufacturing by integrating the conveyor belt into his automotive assembly line. This innovative combination accelerated production and brought a new level of standardization to manufacturing. His approach quickly inspired other industries to adopt and adapt the system for their own use.
For many years, conveyor belts saw little change. Then, in 1957, B.F. Goodrich revolutionized the industry with a rubberized steel belt that far outlasted any before it. This innovation featured a unique half twist that exposed both sides of the surface area, effectively halving the wear on each side. As scientists developed stronger materials, Goodrich engineers responded with even more durable belt designs, eliminating the need for the twist.
In 1970, the American company Intralox secured a patent for the first plastic conveyor belts. Since then, numerous other companies have entered the plastic belt market. Today, conveyor belts come in various rubber and polymer materials, making them versatile enough to operate in countless environments.
Conveyor Belt Design
Typically, conveyor belts are flat and crafted from a flexible material such as rubber. They usually function by being mounted on a series of rollers, which are driven by an electric motor.
Materials
A typical flat belt features multiple layers to enhance durability and resistance to wear. Its core is made from materials such as fabric or wire mesh. Common options include aramid fiber, polyester, cotton, steel, stainless steel, and galvanized steel.
They coat this core with layers on both sides of the mesh. The layers can be crafted from various materials, provided they are durable, strong, and reliable. The material can be either flexible and seamless or composed of a series of lightweight, hard pieces. Typically, they use rubber for the belt, but plastic options like PVC or polyurethane are also common choices.
Design Considerations
When designing conveyor belts, manufacturers take into account various factors, including the type of products or materials being transported, their weight and shape, the length of the conveyor system, any existing equipment that needs to be integrated, the layout and environment of the space, the frequency of use, and the relevant standard requirements (such as FDA, medical grade, or food grade).
Taking these factors into account, manufacturers have numerous decisions to make, such as choosing materials, belt type, size, groove shapes, and construction. For instance, in situations where a conveyor operates against gravity, a belt with ridges can be designed to prevent objects from rolling off during transport. Similarly, for handling heavy loads, a wider belt can be engineered to support the increased weight.
Types of Conveyor Belts
Types of Conveyor Belts: A Comprehensive Guide to Applications and Features
Conveyor belts are essential tools in a wide range of industries, offering efficient solutions for material handling and transportation. Understanding the different types of conveyor belts and their applications can help you select the right system for your operational needs. This guide explores various conveyor belt types, their features, and their uses in industries such as food processing, mining, packaging, and more.
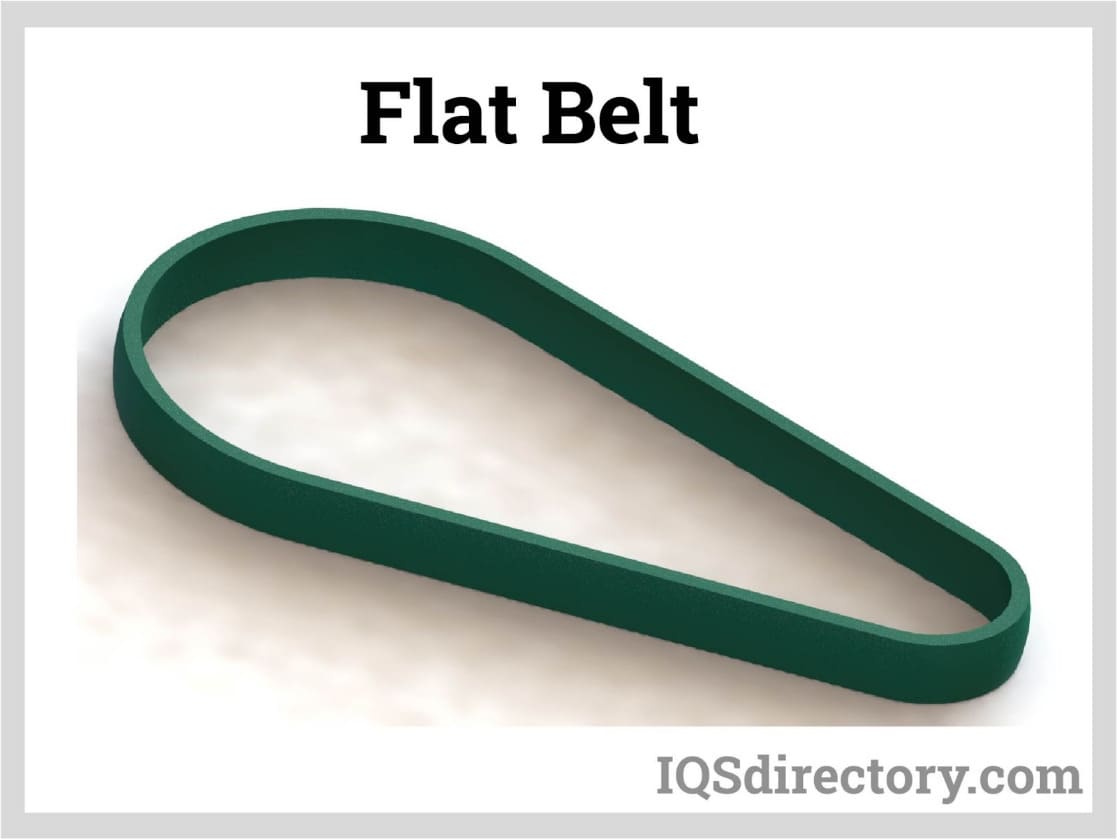
Flat Belts: Versatile and Reliable
Flat belts are continuous, straight belts widely used across industries for their versatility. These belts are ideal for applications like:
- Industrial Coating: Ensuring smooth material application.
- Draining, Heating, Cooling, and Drying: Perfect for processes requiring temperature control.
- Mining and Logging: Handling rugged materials with ease.
Flat belts are crafted from uniform thermoplastics with a seamless design, featuring a fully closed surface to minimize bacterial buildup. This makes them an excellent choice for food processing, including handling raw and cooked meats, fruits, and vegetables.
Continuous Belting: Seamless Efficiency
Also known as endless belting, continuous belting features a seamless, joint-free design. This construction ensures smooth operation and reduces wear, making it ideal for high-speed conveyor systems. Continuous belts enhance reliability in demanding applications where consistent performance is critical.
O-Ring Belts: Flexible and Secure
O-ring belts, also called round belts or endless round belts, are stretchable and versatile components. They are commonly used to:
- Secure flat belts onto rollers or chains, preventing slipping during curves or turns in large conveyor systems.
- Support power transmission systems in various machinery.
O-ring belts are designed for durability and flexibility, ensuring stable performance in complex conveyor setups.
Cotton Conveyor Belts: Lightweight and Food-Safe
Cotton conveyor belts are lightweight, tightly woven fabrics ideal for food processing and baking. These belts can be designed to meet FDA and USDA standards, ensuring safety and hygiene. Cotton belts provide excellent performance in food-grade applications where cleanliness is a priority.
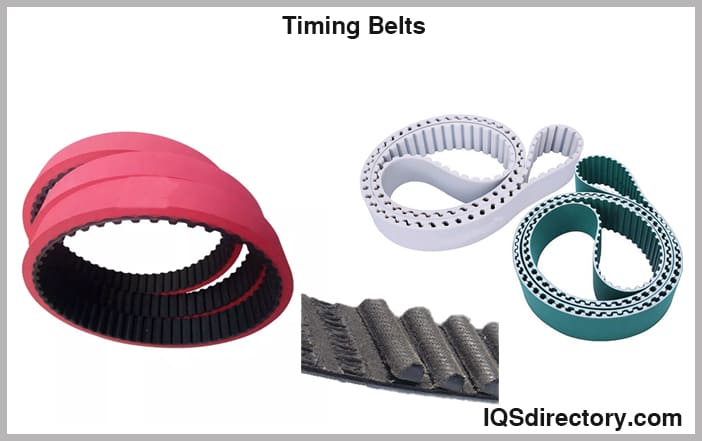
Timing Belts: Precision in Motion
Timing belts are critical in internal combustion engines and manufacturing equipment, working in sync with gears and cogs. They ensure precise timing and movement, making them essential for specialized machinery. Many manufacturers accept custom orders for timing belts tailored to specific equipment or functions.
Fin Belts: Efficient Carton Handling
Fin belts feature fin-like extensions that protrude from the main belt, designed to flex and handle fast-moving containers. These belts are perfect for packaging facilities, where they efficiently separate cartons. Fin belts enhance productivity in high-speed packaging operations by ensuring smooth and controlled movement.
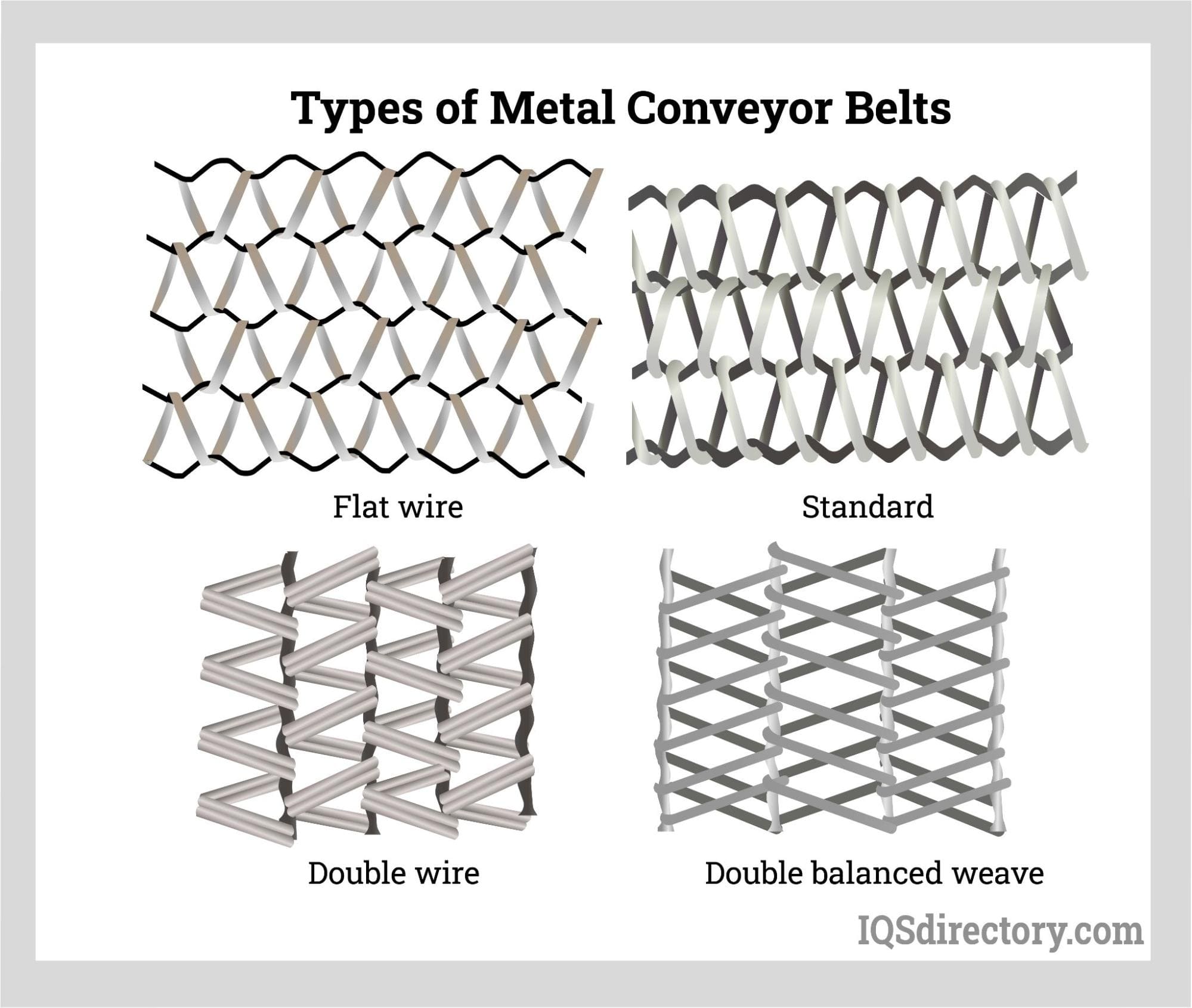
Wire Belts and Wire Mesh Belts: Heavy-Duty and Heat-Resistant
Wire belts are made from woven wire cords, typically steel or stainless steel, or chain mail-like wire links, designed for heavy-duty applications. Wire mesh belts, crafted from stainless steel (series 300), feature a non-exposed hinge mechanism to prevent bacterial buildup. Their exceptional heat resistance and stability make them ideal for:
- Cooking Applications: Handling breaded products.
- High-Temperature Environments: Ensuring durability under extreme conditions.
Wire and wire mesh belts are engineered for reliability in demanding industries like food processing and industrial cooking.
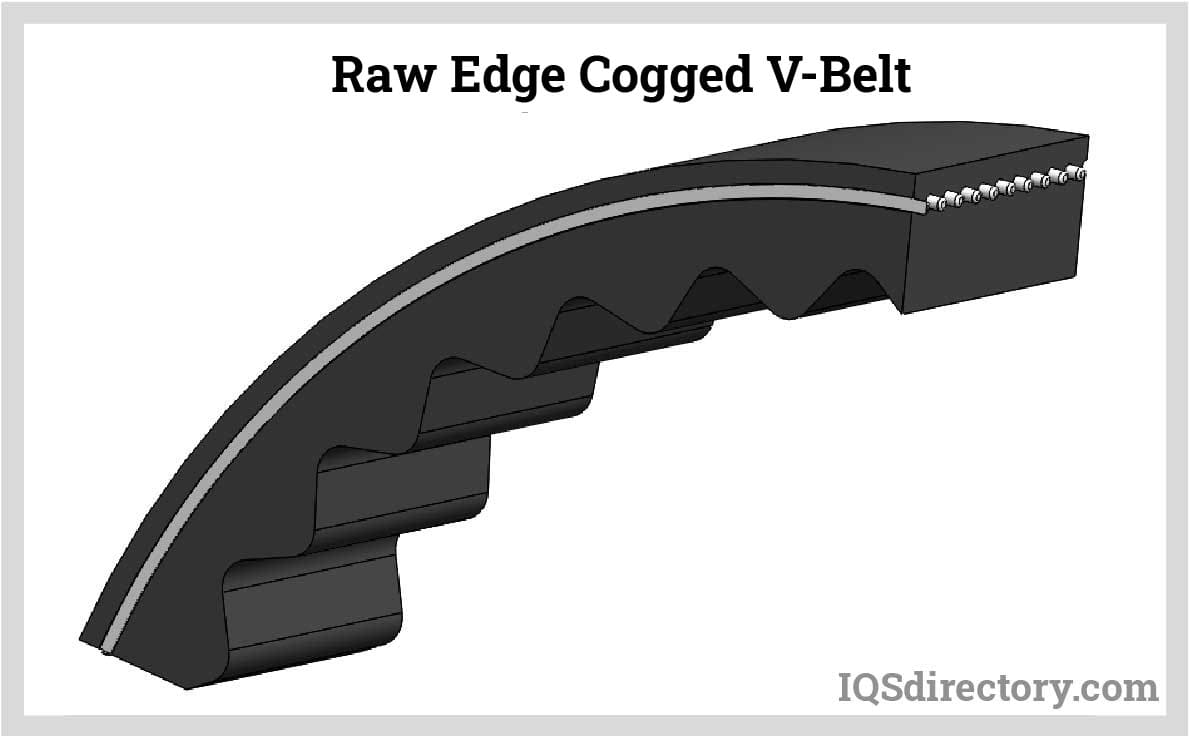
V-Belts: High Torque with Less Tension
V-belts are designed with a V-shaped groove that fits into a pulley, allowing them to transmit higher torque than flat belts with less width and tension. A deeper V slot can enhance grip, making them suitable for lighter applications. V-belts deliver efficient power transmission in various systems, offering a balance of performance and simplicity.
Rubber Conveyor Belts: Versatile and Durable
Rubber conveyor belts are made from natural or synthetic rubber materials, such as urethane, silicone, and neoprene. Available in various thicknesses and grades, these belts are used in:
- Food Transport: Ensuring safe handling.
- Industrial Material Handling: Managing heavy loads.
Rubber belts are designed for versatility and durability, catering to a wide range of industrial needs, from food production to heavy-duty material transport.
Roller Conveyors: Smooth Material Movement
Roller conveyors operate using a series of rollers set within a frame, with the belt resting on top. As the rollers spin, they propel the belt forward, carrying items along. These systems are ideal for moving packages and materials in warehouses and manufacturing facilities, ensuring smooth and efficient material transport.
Choosing the Right Conveyor Belt for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate conveyor belt depends on your industry, application, and operational requirements. Consider factors like:
- Material Type: Rubber, cotton, or wire mesh for specific environments.
- Load Capacity: Heavy-duty belts like steel wire for bulk materials.
- Hygiene Standards: FDA-compliant belts for food processing.
- Environmental Conditions: Heat-resistant belts for high-temperature applications.
Enhance Your Operations with the Right Conveyor Belt
Whether you need a flat belt for food processing, a wire mesh belt for cooking, or a rubber conveyor belt for industrial use, understanding the different types of conveyor belts can help you optimize your operations. By choosing the right belt, you can improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and ensure reliable performance in your facility.
Conveyor Belting Accessories
Enhancing Efficiency and Performance
Conveyor belting systems are vital for efficient material handling across industries like manufacturing, mining, food processing, and logistics. While the conveyor belt itself is the core component, conveyor belting accessories play a crucial role in optimizing performance, ensuring safety, and extending the lifespan of the system. These accessories enhance functionality, improve operational efficiency, and address specific challenges in various applications. This article explores the key conveyor belting accessories, their benefits, and their applications in diverse industries.
What Are Conveyor Belting Accessories?
Conveyor belting accessories are supplementary components designed to support, maintain, and enhance the performance of conveyor systems. These accessories include items like belt fasteners, pulleys, idlers, scrapers, and more, each serving a specific purpose to ensure smooth operation. By integrating the right accessories, businesses can reduce downtime, improve safety, and handle a wide range of materials—from bulk goods to delicate food products.
Key Conveyor Belting Accessories and Their Functions
Here’s a look at some essential conveyor belting accessories and how they contribute to efficient operations:
- Belt Fasteners and Splices
Belt fasteners and splices are used to join the ends of a conveyor belt, creating a continuous loop or repairing damaged sections. They come in various types, including:
- Mechanical Fasteners: Metal hinges or plates that provide a quick, strong connection, ideal for heavy-duty applications like mining.
- Vulcanized Splices: A heat or chemical bonding process that creates a seamless, durable joint, often used in food processing for hygiene.
Benefits: Properly installed fasteners and splices prevent belt slippage, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent material flow.
- Pulleys and Rollers
Pulleys and rollers are critical for driving and guiding the conveyor belt. They include:
- Drive Pulleys: Powered components that move the belt.
- Idler Rollers: Support the belt and the load, reducing friction and wear.
- Return Rollers: Guide the belt back to the starting point.
Benefits: High-quality pulleys and rollers ensure smooth belt movement, reduce energy consumption, and minimize wear on the belt, extending its lifespan.
- Belt Scrapers and Cleaners
Belt scrapers and cleaners remove material buildup from the belt surface, preventing carryback (material that sticks to the belt and falls off later). Types include:
- Primary Scrapers: Positioned at the head pulley to remove bulk material.
- Secondary Scrapers: Installed further along the belt to clean residual fines.
- Brush Cleaners: Use rotating brushes for sticky or fine materials.
Benefits: Cleaners maintain belt hygiene, reduce maintenance costs, and prevent material spillage, which is especially important in food processing and pharmaceutical applications.
- Skirtboards and Skirting Systems
Skirtboards are panels installed along the sides of the conveyor to contain materials and prevent spillage. Skirting systems, often made of rubber or polyurethane, seal the gap between the belt and the skirtboard.
- Applications: Ideal for handling bulk materials like gravel, coal, or grain in mining and aggregate industries.
Benefits: Skirting systems reduce dust, minimize material loss, and enhance safety by keeping materials on the belt.
- Belt Tracking Systems
Belt tracking systems ensure the conveyor belt stays aligned and centered during operation. Misalignment can cause belt damage, material spillage, and downtime. These systems include:
- Tracking Rollers: Automatically adjust the belt’s position.
- Sensors and Guides: Detect and correct misalignment in real time.
Benefits: Proper belt tracking reduces wear, prevents costly repairs, and ensures consistent performance, especially in high-speed or heavy-load applications.
- Impact Beds and Bars
Impact beds and bars are installed at loading zones to absorb the shock of heavy materials dropping onto the belt. They consist of:
- Impact Bars: Made of rubber or polyurethane to cushion the load.
- Impact Beds: A series of bars or rollers designed to distribute impact forces.
Benefits: These accessories protect the belt from damage, reduce maintenance costs, and are essential for industries like mining and construction where heavy materials are common.
- Conveyor Belt Covers and Hoods
Covers and hoods protect the conveyor system from environmental factors like rain, dust, and debris. They are particularly useful for outdoor conveyors in industries like agriculture and mining.
- Types: Full covers, partial hoods, or retractable designs for easy access.
Benefits: Covers extend the belt’s lifespan, reduce maintenance, and ensure consistent operation in harsh conditions.
- Safety Accessories
Safety accessories are designed to protect workers and equipment. These include:
- Emergency Stop Switches: Allow immediate shutdown in case of hazards.
- Belt Rip Detectors: Sensors that detect tears or damage in the belt, preventing further issues.
- Guardrails and Netting: Prevent workers from accessing dangerous areas.
Benefits: Safety accessories reduce the risk of accidents, ensure compliance with regulations, and protect both personnel and equipment.
- Cleats and Sidewalls
Cleats and sidewalls are added to the belt surface to handle inclined or vertical conveying. They prevent materials from slipping back on steep angles.
- Cleats: Raised sections that grip materials.
- Sidewalls: Vertical barriers that contain materials on the belt.
Benefits: These accessories are ideal for food processing (e.g., transporting fruits or vegetables) and bulk material handling (e.g., sand or gravel), ensuring efficient movement on inclines.
Applications of Conveyor Belting Accessories Across Industries
Conveyor belting accessories are tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries:
- Food Processing: Belt scrapers, FDA-compliant splices, and cleats ensure hygiene and efficient handling of food products.
- Mining and Aggregates: Impact beds, skirtboards, and heavy-duty fasteners handle abrasive materials like coal and gravel.
- Packaging: Belt tracking systems and fin belts ensure precise movement of cartons and packages.
- Manufacturing: Pulleys, rollers, and safety accessories support high-speed production lines.
- Agriculture: Covers and cleats protect and transport crops efficiently, even on inclines.
Benefits of Using Conveyor Belting Accessories
- Increased Efficiency: Accessories like tracking systems and pulleys ensure smooth operation, reducing downtime and boosting productivity.
- Extended Belt Lifespan: Impact beds, scrapers, and covers protect the belt from damage, minimizing replacement costs.
- Enhanced Safety: Safety accessories like emergency stops and rip detectors protect workers and equipment.
- Improved Hygiene: Cleaners and seamless splices prevent bacterial buildup, crucial for food and pharmaceutical applications.
- Versatility: Cleats, sidewalls, and custom fasteners allow conveyor systems to handle a wide range of materials and conditions.
Choosing the Right Conveyor Belting Accessories
Selecting the appropriate accessories depends on your industry, material type, and operational environment. Consider the following:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure accessories are suitable for the materials being handled (e.g., food-grade for food processing, heavy-duty for mining).
- Environmental Conditions: Choose weather-resistant covers for outdoor systems or heat-resistant components for high-temperature applications.
- Maintenance Needs: Opt for accessories that reduce maintenance, such as self-cleaning scrapers or durable splices.
- Safety Standards: Prioritize accessories that meet industry safety regulations, especially in high-risk environments.
Optimize Your Conveyor System Today
Conveyor belting accessories are essential for maximizing the performance, safety, and longevity of your conveyor system. By investing in the right components—whether it’s a belt scraper for hygiene, an impact bed for heavy loads, or a tracking system for alignment—you can ensure efficient operations and reduce operational costs. Evaluate your conveyor system’s needs and explore the wide range of accessories available to enhance its functionality for your specific industry.
Proper Care for Conveyor Belts
To start properly maintaining your conveyor belt, focus on its usage. Use the belt only within its designed limits—avoid placing loads that exceed its weight capacity and ensure that all substances are compatible with the belt material.
Alongside this, you must regularly check your belt for contaminants such as dirt and dust, and for signs of wear and tear or improper adjustment. A misaligned belt is vulnerable to ripping, twisting, and slipping. If it’s allowed to operate while misaligned, it can become loose or stretched, leading to decreased quality, inefficiency, and potential accidents. Proper tensioning of the belt is also essential.
Ensuring proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of your conveyor belt. Lubrication helps prevent wear on the moving parts and shields them from contaminants. However, even if contaminants don’t directly touch the surfaces, they can still cause issues. To further protect your equipment, we suggest incorporating an air quality maintenance system or a dust collection system.
Conveyor Belting Standards
The quality standards for your conveyor belts will vary based on your application, industry, and location. For instance, if you’re conveying food, your belt needs to be food-grade or FDA compliant. Similarly, for agricultural materials, USDA compliance is required. To determine the specific standards applicable to your belting needs, consult with industry experts.
Things to Consider About Conveyor Belting
Numerous manufacturers provide a range of conveyor belts, including custom options, standard models, discounted surplus, and used varieties. The best choice for us hinges on our specific application and budget. To assist in our decision-making, we’ve compiled a list of reputable conveyor belt manufacturers and suppliers on this page. Explore their profiles and websites to discover what they offer.
Conveyor Belt Splices- Conveyor belt splicing involves connecting two segments of a conveyor belt to extend its length or mend any damage. Various splicing methods exist, with the appropriate choice depending on the belt’s type, its speed, and the materials it transports. Selecting the right, high-quality splice for your system is crucial to avoid potential financial setbacks from repairs.
Mechanical Splicing- They use a mechanical splicing system to join belts using metal fasteners, hinges, or plates, ensuring strong, dependable connections. This technique is versatile, suitable for various belt types and environments, and is especially favored in industries such as mining and quarrying. Here are some important considerations when deciding to use this option:
- Mechanical splices are straightforward to install. With portable tools, an installation crew can fit the splices in under an hour, depending on the belt’s width and thickness.
- Temperature, moisture, and contaminants do not impact the installation of mechanical splices.
- This splicing method minimizes belt waste and its visibility on the belt facilitates easier inspection.
- Since they can easily spot material wear, they can perform preventive maintenance earlier, reducing the risk of breakdowns during crucial operations.
Vulcanized Splicing- Also known as chemical splicing, this intricate procedure utilizes heat and/or chemicals to join belts for lengthening or repair. It demands specialized skills and equipment. Additionally, environmental factors such as temperature and moisture must be considered. Despite being challenging and costly, vulcanized splices typically result in smoother and more durable connections compared to mechanical splices. There are two types of vulcanization: hot and cold.
- Hot vulcanization utilizes heat and pressure applied through a vulcanizing press. While this method can be time-consuming, often requiring several hours, it results in stronger, longer-lasting splices compared to other techniques.
- Cold vulcanization is a reliable technique that employs chemicals to bond two pieces of belt together. This method requires specialized hand tools and top-notch bonding agents.
Conveyor belts will always be a primary choice in bulk materials handling. Their capability to safely manage large quantities of material in an organized and timely manner makes them an essential component of industrial production. Ensure that the parts of your conveyor, such as its splices, belt, motor, pulleys, and metal or rubber-based rollers, are constructed from high-quality materials.
To streamline your search, we suggest taking a moment to jot down your specifications, requirements, and questions. Remember to include your budget, quality standards, delivery deadlines, and support preferences, such as installation assistance and parts replacement. Once your list is ready, start your search. The manufacturers we’ve listed are experienced and trustworthy, but only one will be the perfect fit for you. Identify three or four that stand out and reach out to each with your list. After discussing your needs with them, compare their services and offers to find the one that suits you best.
Choosing the Right Conveyor Belt Supplier via IQSdirectory.com
Selecting the right conveyor belt supplier is a critical decision for businesses that rely on efficient material handling systems. Conveyor belts are essential in industries like manufacturing, mining, food processing, logistics, and more, where they streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and enhance productivity. A reliable supplier ensures that your conveyor system operates seamlessly, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Drawing on insights from industry resources like IQS Directory, this guide outlines key factors to consider when choosing a conveyor belt supplier to meet your operational needs.
- Assess Product Quality and Durability
The quality of the conveyor belts is paramount, as it directly impacts the efficiency and longevity of your system. High-quality belts withstand the rigors of daily use, reducing wear and tear, and minimizing disruptions. When evaluating suppliers:
- Look for Durable Materials: Suppliers should offer belts made from robust materials like rubber, polyurethane, stainless steel, or fabric, depending on your application. For example, rubber belts are versatile for industrial use, while stainless steel is ideal for high-temperature or food-grade applications.
- Check Compliance with Standards: Ensure the supplier adheres to national and international standards, such as FDA or USDA regulations for food processing belts, or ISO standards for industrial applications. This guarantees safety and reliability.
- Evaluate Belt Specifications: Consider the belt’s tensile strength, cover thickness, and resistance to environmental factors like heat, cold, or chemicals. For instance, a heat-resistant belt is crucial for high-temperature environments, while an oil-resistant belt suits oily conditions.
A supplier offering a wide range of durable, high-quality belts tailored to specific needs is a strong candidate.
- Evaluate Industry Experience and Expertise
Experience matters when selecting a conveyor belt supplier. A supplier with a proven track record in your industry is more likely to understand your unique challenges and requirements. Here’s what to look for:
- Industry-Specific Knowledge: Choose a supplier with experience serving industries similar to yours. For example, a supplier familiar with food processing will know the importance of hygienic, easy-to-clean belts, while one experienced in mining will prioritize heavy-duty belts for abrasive materials.
- Technical Expertise: The supplier should have knowledgeable staff who can provide guidance on belt selection, customization, and troubleshooting. They should understand the nuances of different conveyor systems, from troughed belt conveyors to modular belt systems.
- Case Studies and References: Ask for examples of successful installations or client testimonials. A supplier with a history of solving complex conveyor challenges demonstrates reliability and expertise.
Suppliers listed on platforms like IQS Directory often highlight their experience and industry focus, making it easier to identify those with relevant expertise.
- Consider Customization Capabilities
No two operations are identical, and your conveyor system may require tailored solutions to maximize efficiency. A good supplier should offer customization options to meet your specific needs:
- Custom Belt Design: Look for suppliers who can manufacture belts with specific features, such as cleats, sidewalls, or unique patterns (e.g., chevron or fan-shaped patterns) for inclined transport or anti-slip functionality.
- Size and Configuration: Ensure the supplier can provide belts in the right width, length, and configuration for your system. Common widths range from 500 mm to 1400 mm, but custom sizes may be necessary for unique setups.
- Material Options: The supplier should offer a variety of materials to suit your application, such as polyurethane for high tensile strength, fabric for low-friction needs, or steel for heavy-duty tasks.
Customization ensures your conveyor system aligns with your operational goals, whether you’re handling delicate food products or heavy aggregates.
- Check for Fast Delivery and Reliable Service
Downtime can be costly, so a supplier’s ability to deliver products quickly and provide reliable service is crucial. Consider the following:
- Delivery Times: Suppliers should offer fast delivery to minimize disruptions. Platforms like IQS Directory often highlight suppliers known for quick turnaround times, which is essential for urgent replacements or new installations.
- Service and Support: Look for suppliers who provide robust after-sales support, including installation assistance, troubleshooting, and maintenance services. Access to service crews for emergency repairs or preventative maintenance can significantly reduce downtime.
- Spare Parts Availability: Ensure the supplier has quick access to spare parts like pulleys, rollers, or fasteners. This is critical for minimizing delays during repairs.
A supplier that prioritizes fast delivery and comprehensive support helps keep your operations running smoothly.
- Review Reputation and Customer Feedback
A supplier’s reputation can provide valuable insight into their reliability and service quality. Here’s how to assess this:
- Customer Reviews: Look for positive feedback from other businesses. Suppliers with strong recommendations are more likely to deliver quality products and services.
- Industry Standing: A supplier with a long history and a strong presence in the industry, as often showcased on directories like IQS Directory, is typically a safer choice.
- Partnership Approach: Choose a supplier that values long-term partnerships. They should be proactive in understanding your needs, offering solutions, and providing ongoing support to drive mutual success.
A reputable supplier with a customer-centric approach ensures a reliable, collaborative relationship.
- Balance Cost with Quality
While cost is an important factor, it shouldn’t be the sole deciding factor. A cheap belt may lead to frequent replacements and repairs, ultimately costing more in the long run. Instead:
- Evaluate Long-Term Value: Consider the belt’s expected lifespan and maintenance requirements. A higher-quality belt may have a higher upfront cost but can save money by reducing downtime and replacements.
- Compare Quotes: Request custom quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing. Many suppliers on IQS Directory offer competitive pricing and the ability to provide quick quotes.
- Look for Cost-Saving Features: Some belts, like modular plastic belts, are designed for easy repair and replacement of segments, reducing long-term costs.
Balancing cost with quality ensures you invest in a conveyor system that delivers lasting value.
- Ensure Compatibility with Your System
The supplier should provide belts and components that integrate seamlessly with your existing conveyor system. Consider:
- System Specifications: Ensure the supplier can provide belts that match your system’s pulleys, rollers, and frame. For example, a troughed belt conveyor requires a belt that fits its rollers to prevent spillage.
- Advanced Features: If your system uses sensors, robotics, or automation software, the supplier should offer belts that support these technologies, such as belts with low vibration or high precision for automated processes.
- On-Site Support: Some suppliers offer surveys and inspections of your facility to ensure compatibility and recommend the best products for your setup.
Compatibility minimizes operational disruptions and ensures optimal performance.
Additional Tips for Choosing a Supplier
- Training and Support: Some suppliers provide on-site training for your staff on belt maintenance, safety, and troubleshooting. This empowers your team to handle minor issues independently.
- Environmental Considerations: If your facility operates in extreme conditions (e.g., high humidity, low temperatures), choose a supplier with belts designed for those environments, such as cold-resistant or acid-resistant belts.
- Innovation and Technology: Suppliers who invest in advanced technology, like eco-friendly materials or belts with enhanced tensile strength, can offer superior products that improve efficiency.
Why Choosing the Right Supplier Matters
A reliable conveyor belt supplier is more than just a vendor—they’re a partner in your operational success. The right supplier ensures:
- Minimized Downtime: High-quality belts and fast service reduce interruptions.
- Cost Savings: Durable products and efficient support lower long-term costs.
- Improved Productivity: A well-suited conveyor system enhances workflow and throughput.
- Safety and Compliance: Belts that meet industry standards protect your workers and products.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right conveyor belt supplier requires careful consideration of factors like product quality, industry experience, customization capabilities, delivery speed, reputation, cost, and system compatibility. By prioritizing these elements, you can find a supplier that meets your needs and supports your operational goals. Platforms like IQS Directory can be a valuable resource, connecting you with top conveyor belt manufacturers and suppliers who offer durable solutions, competitive pricing, and fast delivery. Take the time to evaluate your options, request quotes, and build a partnership that drives efficiency and success in your material handling operations.
What is a conveyor belt system and how does it work?
A conveyor belt system is a mechanical assembly designed to move goods, products, or materials from one point to another within a facility. It consists of a belt looped around two or more pulleys and is powered by a motor. The belt, made from materials such as rubber, fabric, metal, or plastic, continuously moves and carries items efficiently, reducing manual labor and speeding up processes in industries such as automotive, mining, food processing, and more.
What are the main types of conveyor belts and their applications?
Main types of conveyor belts include flat belts for general material handling and food processing, plastic modular belts ideal for flexible manufacturing and food hygiene, wire mesh belts for high-temperature or heavy-duty applications, timing belts for synchronized operations, and V-belts for high-torque transmission. Each type is suited to specific industries such as mining, packaging, food processing, and manufacturing, depending on the material, weight, and operational requirements of the conveyed items.
Which industries commonly rely on conveyor belting systems?
Industries that commonly use conveyor belting systems include food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, waste management, mining, automotive assembly, electronics manufacturing, printing, and packaging. These industries depend on conveyor belts to facilitate efficient, sanitary, and streamlined transport of materials or products throughout production and distribution processes.
What are common conveyor belting accessories and their purposes?
Conveyor belting accessories include belt fasteners and splices for joining ends or repairs, pulleys and rollers for driving and guiding the belt, belt scrapers and cleaners to remove build-up, skirtboards and skirting systems to contain materials, belt tracking systems to maintain alignment, impact beds and bars to absorb shock in loading zones, conveyor belt covers for environmental protection, safety accessories such as emergency stops, and cleats or sidewalls for handling inclined transport. These components improve efficiency, extend belt lifespan, and enhance safety.
How should conveyor belts be maintained for optimal performance?
To maintain conveyor belts, regularly inspect for contaminants, wear, and misalignment. Use the belt within its designed load and environmental limits. Proper tensioning and lubrication are essential for smooth operation and longevity. Implementing dust collection systems and maintaining belt splices will further reduce the risk of damage and downtime, ensuring continuous and safe system operation.
What are the primary conveyor belt splicing methods and their differences?
The two main splicing methods are mechanical splicing and vulcanized splicing. Mechanical splicing uses metal fasteners or hinges for a quick and easy connection, suitable for various environments and allows easy inspection. Vulcanized splicing uses heat or chemicals to bond belt segments, creating a smoother and more durable joint but requires specialized equipment and skills. Vulcanized splicing includes both hot (using heat and pressure) and cold (using chemicals) methods.
How do you choose the right conveyor belt supplier?
To choose the right conveyor belt supplier, assess product quality, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Consider the supplier’s experience, customization capabilities, delivery speed, reputation, and after-sale support. Balance cost with long-term value and ensure belt compatibility with your existing system. Suppliers listed on reputable directories often specialize in meeting the needs of specific industries and offer resources for comparison and evaluation.







 Conveyor Belting
Conveyor Belting Conveyor Systems
Conveyor Systems Conveyors
Conveyors Hosereels
Hosereels Industrial Lubricants
Industrial Lubricants Lubricators
Lubricators Screw Conveyors
Screw Conveyors Pneumatic Conveyors
Pneumatic Conveyors AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches